Notes from daily Drishti IAS Current Affairs arranged in the mind map form, which helps students in retaining information without losing any key points. Credits for the main contents belongs to the Drishti IAS Current Affairs.
Table of Contents
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: UNEP’s Action Plan for Cooling Sector
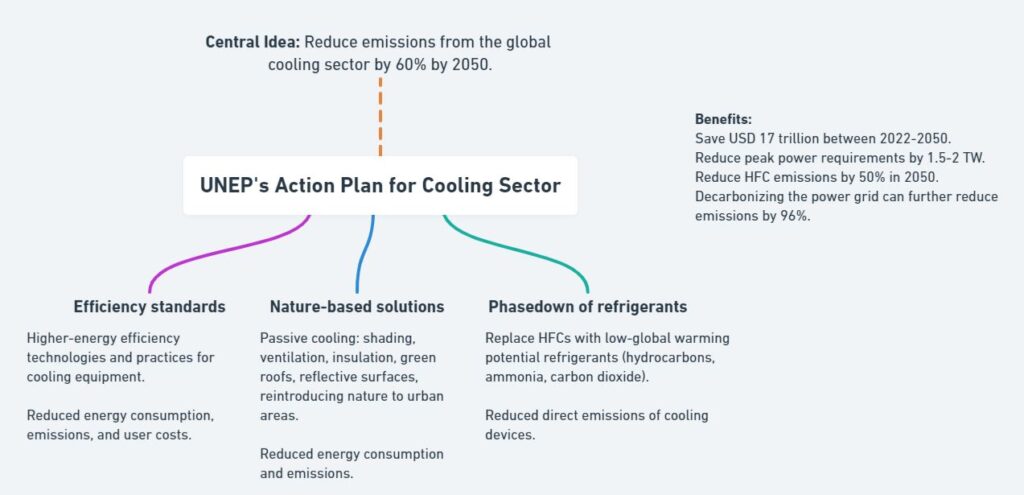
Central Idea: Reduce emissions from the global cooling sector by 60% by 2050.
Why in News?
Cooling sector accounts for 20% of global electricity consumption and is projected to triple by 2050.
Current trends could lead to emissions of 4.4-6.1 billion tonnes of CO2e by 2050 (>10% of global projected emissions).
Action Plan
Nature-based solutions:
Passive cooling: shading, ventilation, insulation, green roofs, reflective surfaces, reintroducing nature to urban areas.
Reduced energy consumption and emissions.
Efficiency standards:
Higher-energy efficiency technologies and practices for cooling equipment.
Reduced energy consumption, emissions, and user costs.
Phasedown of refrigerants:
Replace HFCs with low-global warming potential refrigerants (hydrocarbons, ammonia, carbon dioxide).
Reduced direct emissions of cooling devices.
Benefits:
Save USD 17 trillion between 2022-2050.
Reduce peak power requirements by 1.5-2 TW.
Reduce HFC emissions by 50% in 2050.
Decarbonizing the power grid can further reduce emissions by 96%.
- Related initiatives:
National Cooling Action Plans (NCAPs): Implemented by 40+ countries, including India.
Global Cooling Pledge: Launched by UAE and Cool Coalition, signed by 60+ countries.
Kigali Amendment Acceleration: Aims to reduce HFC production and consumption by 80-85% by 2047.
India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP): Led by Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- Additional notes:
India has a slow NCAP rollout despite implementation mechanisms.
The Cool Coalition is a global network of partners working for efficient, climate-friendly cooling.
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Critical Minerals: India’s Opportunity
Central Idea: India launches first auction of critical minerals, emphasizing their importance for economic development, national security, and environmental sustainability.
Why in News?
First auction of critical minerals including lithium, nickel, copper, molybdenum, and rare earth elements across 8 states.
Follows declaration of 30 minerals as “critical” and amendments to mining laws.
Key Features of the Auction:
First auction of mining rights for lithium ore.
Mining Licences (ML) for immediate mining and Composite Licences (CL) for exploration before mining.
Bidding based on highest percentage of mineral dispatch value.
Second tranche of auctions anticipated.
Background:
30 minerals declared “critical” in July 2023.
Geological Survey of India actively exploring critical mineral reserves.
What are Critical Minerals?
Minerals which are:
a. Essential for economic development and national security.
b. Supply chain vulnerabilities due to limited availability and concentrated extraction/processing.
c. Dynamic list evolving with new technologies, market dynamics, and geopolitical considerations.
Significance Critical Minerals for India
Economic Development:
High-tech industries rely on critical minerals.
Green technologies like solar panels, wind turbines, batteries, and electric vehicles.
Job creation, income generation, and innovation.
National Security:
Vital for defense, aerospace, nuclear, and space applications.
High-quality materials for extreme conditions and complex functions.
Environmental Sustainability:
Integral to clean energy transition and low-carbon economy.
Essential for achieving India’s renewable energy goals.
Challenges:
Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Disruptions to critical mineral supply chains.
Limited Domestic Reserves: Heavy reliance on imports.
100% import reliance for lithium and nickel, 93% for copper.
Increasing Demand for Minerals: Renewable energy and electric vehicle technologies.
Opportunities:
Strategic management of critical minerals.
International cooperation and partnerships.
Mineral Security Partnership (MSP) led by the United States.
Bilateral agreements with resource-rich countries.
Australia, Canada, Japan, South Africa.
Conclusion:
Critical minerals crucial for India’s economic, security, and environmental goals.
First auction marks a significant step towards securing supplies.
Strategic management and international cooperation are key to achieving self-sufficiency and leadership in this critical sector.
UPSC Previous Year Question (PYQ)
1. Despite India being one of the countries of Gondwanaland, its mining industry contributes much less toits Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in percentage. Discuss. (2021)
2. “In spite of adverse environmental impact, coal mining is still inevitable for development”. Discuss.(2017)
Suggested Read: Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Free Notes Dec 7,2023
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Jammu and Kashmir Bills 2023
Central Idea: Lok Sabha passes two bills related to Jammu and Kashmir: Reservation Bill and Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill.
Why in News?
Increase in J&K Assembly seats from 107 to 114.
Reservation for Kashmiri migrants and displaced persons from PoK.
Change in nomenclature for “weak and underprivileged classes” to “other backward classes”.
What is Jammu & Kashmir Reservation (Amendment) Bill, 2023?
a. Amends Section 2 of the Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Act, 2004.
b. Provides reservation for SCs, STs, and “other backward classes” in jobs and professional institutions.
c. Changes the term “weak and underprivileged classes” to “other backward classes”.
What is Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2023?
It amends the 2019 Act and provides representation in the Legislative Assembly for:
a. Kashmiri migrants (two members, one woman)
b. Displaced persons from PoK (one member)
c. Increases total Assembly seats from 107 to 114.
d. 7 seats reserved for SCs
e. 9 seats reserved for STs
f. 24 seats remain vacant until PoK occupation ceases.
g. Effective Assembly strength increases from 83 to 90.
Background:
Delimitation commission formed in March 2020.
Delimitation process concluded, increasing Assembly seats.
Zero Terror Plan:
Comprehensive strategy to eradicate terrorism in J&K.
Abrogation of Article 370 contributed to decline in terrorism.
Significance:
Addressing concerns of marginalized communities.
Increased representation for various groups.
Potential positive impact on socio-economic development.
Challenges:
Ensuring fair and equitable implementation.
Addressing potential political tensions.
Maintaining peace and security in the region.
Conclusion:
These bills represent significant steps towards inclusivity and representation in Jammu and Kashmir. However, successful implementation and long-term impact will depend on addressing potential challenges and ensuring a peaceful and stable environment.
What is Delimitation?
a. Fixing or redrawing constituency boundaries based on population size.
b. Independent Delimitation Commission conducts the exercise.
c. Redefining constituency areas and number of seats.
d. Reservation of Assembly seats for SC & ST.
UPSC Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims:
1. With reference to the Delimitation Commission consider the following statements: (2012)
The orders of the Delimitation Commission cannot be challenged in a Court of Law. When the orders of the Delimitation Commission are laid before the Lok Sabha or State Legislative Assembly, they cannot effect any modification in the orders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
2. Which one of the following is the largest (area wise) Lok Sabha constituency? (2008)
(a) Kangra
(b) Ladakh
(c) Kachchh
(d) Bhilwara
Ans: (b)
2. Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
Ans: (d)
Mains:
1. To what extent is Article 370 of the Indian Constitution, bearing marginal note “Temporary provisionwith respect to the State of Jammu and Kashmir”, temporary? Discuss the future prospects of thisprovision in the context of Indian polity. (2016)
2. The banning of ‘Jamaat-e-Islami’ in Jammu and Kashmir brought into focus the role of over-groundworkers (OGWs) in assisting terrorist organizations. Examine the role played by OGWs in assisting terroristorganizations in insurgency-affected areas. Discuss measures to neutralize the influence of OGWs. (2019)
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Decoding Online Gaming Ethics
Central Idea: Online gaming industry adopts voluntary code of ethics to self-regulate and address ethical concerns.
Why in News?
Self-regulatory code signed by IAMAI, EGF, and AIGF.
Focus on responsible practices, consumer protection, and healthy gaming environment.
Key Features of the Code:
KYC procedures for users.
Transparency in winner selection, fees, and deposit usage.
Responsible gaming practices encouraged.
Legal Framework:
Public Gambling Act, 1867: Primarily addresses physical gambling but applicable to online gaming.
Information Technology Act, 2000:
Section 66: Computer-related offenses.
Sections 67, 67A, and 67B: Empower authorities to regulate online gaming.
Self-Regulatory Bodies: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology permits establishment.
Inter-Ministerial Task Force Recommendations: Aim to balance industry growth and consumer protection.
Way Forward:
Technology Integration for Compliance:
Utilize blockchain or other secure technologies for transparency.
Regular Audits and Reporting:
Audits by independent bodies to ensure compliance.
Public reports on winners, fees, and deposit usage.
Consumer Feedback Mechanism: Collect and address player feedback to improve the code.
International Best Practices Adoption:
Learn from successful practices in other jurisdictions.
Participate in global forums for knowledge sharing.
Conclusion:
The voluntary code of ethics represents a significant step towards self-regulation and ethical practices in the online gaming industry. However, successful implementation and long-term impact depend on technology integration, regular audits, consumer feedback mechanisms, and adoption of best practices.
UPSC Previous Year’s Question (PYQs):
1. Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
1. Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
2. Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
3. Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Article 99 of the UN Charter
Central Idea: UN Secretary-General invokes Article 99 to warn the Security Council about the threat to international peace and security in Gaza.
Why in News?
Antonio Guterres highlights the danger posed by Israel’s actions in Gaza.
Aims to prevent a major humanitarian disaster in the region.
What is Article 99?
Provision within the UN Charter, the organization’s constitution. It Empowers the Secretary-General to bring matters threatening international peace and security to the Security Council’s attention.
Discretionary power, allowing the Secretary-General to prioritize critical issues.
Requires the Security Council’s attention when invoked.
Used sparingly (e.g., Congo crisis in 1960, Tunisia-France conflict in 1961, Bangladesh creation in 1971).
Charter of the United Nations:
Founding document of the UN, signed in 1945 and came into force in 1945.
Enables the UN to address various issues due to its international character and Charter-vested powers.
Considered an international treaty, binding on UN Member States.
The International Court of Justice (ICJ), the UN’s primary judicial body, operates by its Statute, annexed to the Charter.
Significance:
Raises awareness of a potentially catastrophic situation in Gaza.
Calls for immediate action by the Security Council to prevent further escalation and humanitarian crisis.
Challenges:
Security Council’s potential inaction due to political considerations.
Difficulty in enforcing resolutions against powerful nations like Israel.
Conclusion:
Invoking Article 99 is a significant step by the UN Secretary-General to address the critical situation in Gaza. While the impact remains to be seen, it underscores the need for urgent international attention and action to avert a humanitarian disaster and ensure lasting peace and security in the region.
Additional Notes:
Consider including specific details about the current situation in Gaza, such as casualties and humanitarian needs.
Mention the possible consequences of inaction by the Security Council.
Discuss potential solutions and the role of the international community in resolving the conflict.
UPSC Previous Year Questions:
Prelims:
Q. The Security Council of UN consists of 5 permanent members, and the remaining 10members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of (2009)
(a) 1 year
(b) 2 years
(c) 3 years
(d) 5 years
Ans: (b)
Mains:
1. What are the main functions of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)? Explaindifferent functional commissions attached to it. (2017)
India Offers Agricultural Line of Credit to Kenya
Central Idea: India extends $250 million line of credit to Kenya for agricultural modernization.
Why in News?
Announcement during Kenyan President’s visit to India.
Aims to strengthen bilateral ties and support Kenya’s agricultural sector.
Key Highlights of the Visit:
Five pacts signed covering sports, education, digital solutions, and maritime cooperation.
Discussion on defense collaboration, trade, energy, healthcare, and public infrastructure.
Invitation to Indian companies to invest in Kenya (agriculture, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals).
Commitment to enhanced counter-terrorism cooperation.
Key Points about Kenya
Location: East Africa
Terrain: Coastal plain, mountains, plateaus
Diverse culture with many ethnic groups and languages
Historical significance: early human ancestor remains discovered, Lake Turkana.
Host to UN-Habitat headquarters.
Line of Credit:
Predetermined borrowing limit accessible as needed.
Funds can be withdrawn and repaid within the limit, allowing repeated use (open line of credit).
Significance:
Boosts India-Kenya relations and cooperation across various sectors.
Supports Kenya’s agricultural modernization efforts.
Creates opportunities for Indian companies to invest in Kenya’s growing economy.
Contributes to regional stability and security through counter-terrorism cooperation.
Additional Notes:
Mention specific areas of agricultural modernization targeted by the line of credit.
Highlight potential benefits for Indian companies investing in Kenya.
Discuss the broader context of India’s engagement with Africa.
Conclusion:
India’s line of credit to Kenya signifies a deepening partnership and commitment to supporting mutual economic development and regional stability. This initiative holds promise for enhancing agricultural productivity, fostering investment, and addressing shared challenges.
You may like this: A Tough Road Ahead for Revanth Reddy as Telangana’s New Chief Minister
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: New AICTE Regulations: 2024-25
Central Idea: AICTE introduces new regulations for undergraduate courses like BBA and BCA, expanding access and enhancing technical education.
Key Highlights
Regulation Expansion:
BBA and BCA programs come under AICTE’s umbrella.
Engineering colleges can offer BBA and BCA programs.
Institutional Flexibility:
Extension of approval up to 3 years for well-performing institutions.
Career Advancement for Working Professionals:
Flexible study timings for selected institutes.
Lateral entry into engineering degrees for diploma graduates.
300+ institutes offering limited seats for working professionals.
Relaxation in ranking criteria for regions lacking suitable institutes.
Regional Language Emphasis:
AICTE publishes textbooks in 13 regional languages.
Polytechnic Autonomy and Industry Collaborations:
Granting autonomy to polytechnic colleges.
Encouraging collaborations with industries for degree issuance and placements.
Significance:
Enhances access to technical education.
Promotes industry-aligned curriculum and skill development.
Improves employability of graduates.
Encourages regional language education in technical fields.
Challenges:
Ensuring quality standards across diverse institutions.
Addressing potential infrastructural and faculty resource limitations.
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of new regulations.
Conclusion:
The new AICTE regulations represent a positive step towards modernizing technical education and enhancing its relevance to industry needs. These changes offer greater opportunities for students and promote professional development for working professionals. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, resource allocation, and ongoing monitoring to ensure quality and meet the evolving needs of the workforce.
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Ban on Sugarcane Juice for Ethanol
Background:
Centre bans sugarcane juice and sugar syrup for ethanol production in 2023-24.
Aims to maintain sugar availability and stabilize prices.
ISMA forecasts 9% reduction in sugar production.
Significance:
India is world’s largest sugar producer, consumer, and 2nd largest exporter.
This ban may affect sugar availability and prices.
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Advancements in TB Care
Background:
Union World Conference on Lung Health unveils 4 new TB drugs.
Reduce treatment time for drug-resistant TB.
Aim to address long treatment duration and drug toxicity.
Significance:
Offers more effective treatment with shorter duration.
May improve patient adherence and reduce drug resistance.
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Hanukkah

Background:
Jewish holiday celebrating rededication of Second Temple.
Begins on 7th December 2023.
Celebrates the miracle of oil lasting eight days.
Significance: Eight-day festival of lights with traditions like lighting menorahs.
Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Central Tribal University in Telangana
Background:
Lok Sabha passes bill establishing central tribal university.
Fulfills obligation of Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act.
₹889.7 crore allocated for the university.
Significance:
University will focus on tribal art, culture, technology, and knowledge.
Aims to improve education and research for tribal communities.


