Notes from daily Vision IAS Current Affairs arranged in the mind map form, which helps students in retaining information without losing any key points. Credits for the main contents belongs to the Vision IAS Current Affairs.
Table of Contents
Suggested Read: Drishti IAS Current Affairs: Free Notes
1. Vision IAS Current Affairs: Kala-Azar Elimination in India
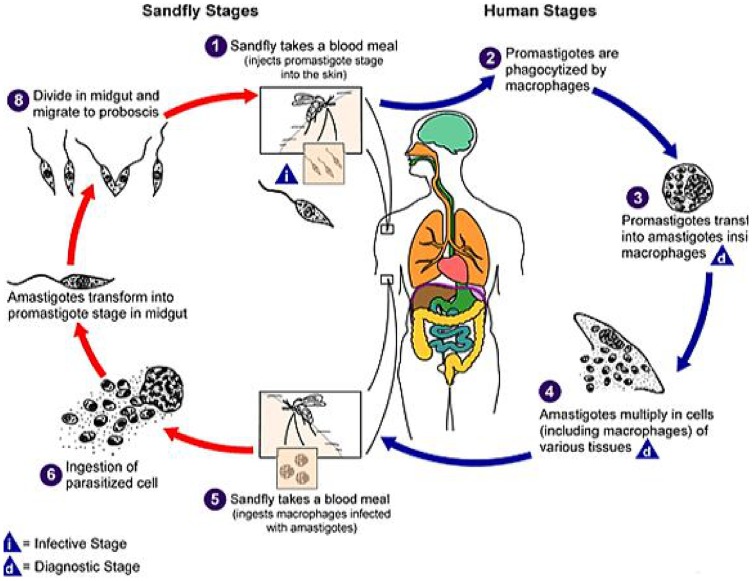
Central Idea: India Nears Elimination of Kala Azar
Key Facts and Stats:
Cases: 530 cases and 4 deaths in 2023 (down from previous years)
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL): 286 cases
Treatment:
Kala-azar: Injectable liposomal amphotericin B
PKDL: 12 weeks of oral miltefosine
Target: Eliminate Kala-azar by 2023
About Kala-Azar:
Caused by Leishmania donovani parasite
Transmitted by sandflies
Symptoms: fever, weight loss, enlarged spleen and liver Fatal if untreated (95%)
Recorded Cases in India: Steady decline in cases and deaths
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL):
Skin lesions caused by Leishmania donovani
Can occur after Kala-azar treatment or independently
Requires separate treatment
Treatment:
Effective drugs available for both Kala-azar and PKDL
Importance of completing treatment
Strategies for Elimination
Effective Spraying
- Control sand fly breeding
- Wall Plastering: Minimize breeding areas
- Treatment Compliance: ASHA network support
Government Initiatives
- Centrally sponsored Kala-azar control Programme
- National Health Policy targets
- Elimination goal set for 2023
Additional Information
- Bangladesh: First country to eliminate Kala-azar
- World Health Organization (WHO) target: 2030Neglected Tropical Diseases Roadmap includes elimination goal
2. Vision IAS Current Affairs: SC Verdict on Revocation of Article 370
Central Idea: SC Upholds Abrogation of Article 370
Key Facts and Stats:
Revocation: August 5, 2019
Cases: 530 cases and 4 deaths (down from previous years)
Union Territory: Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh
Articles: 370, 371, 371A- I, 367
Legislative Assembly: 5-year term
SC Judgement:
Jammu and Kashmir did not possess sovereignty:
Article 370(1) and J&K Constitution show merger agreement not needed.
Article 370 applied Article 1 (J&K as Part III State) with no modifications.
J&K Constitution recognizes itself as integral part of India.
Absence of reference to sovereignty in J&K Constitution preamble.
Article 370 is a temporary provision:
Placed with temporary and transitional provisions in Part XXI.
Instrument of Accession (IoA) shows Article 1 applies to J&K.
Constitutional validity of Proclamations under President’s Rule:
President has power to make irreversible changes, including dissolving Assembly.
Powers subject to judicial and constitutional scrutiny.
The Constitution of J&K stands inoperative:
No longer necessary for J&K Constitution to exist.
Indian Constitution applies in its entirety to J&K.
Set up a Truth and Reconciliation Commission:
Investigate human rights violations by both state and non-state actors.
Special Status of J&K:
Abolished on August 5, 2019:
No separate constitution, flag, or anthem.
No dual citizenship.
Fundamental Rights enshrined in Indian Constitution now apply.
Article 360 (Financial Emergency) now applies.
All laws passed by Parliament apply, including RTI and RTE.
Indian Penal Code replaces Ranbir Penal Code.
Article 35A stands null and void.
Created Union Territories:
Jammu and Kashmir (with Assembly).
Ladakh (without Assembly).
Legal Challenges
Presidential order lacked recommendation of Constituent Assembly:
Government added sub-clause to Article 367 to replace “Constituent Assembly” with”Legislative Assembly”.
No two-thirds majority in Parliament for Constitutional Amendment:
Government argued Article 370 is a temporary provision.
Article 35A added only through Presidential Order:
Government argued it was a valid exercise of power under Article 370.
Conversion into UT violated Article 3:
Government argued Presidential order had Governor’s concurrence.
Instrument of Accession argument:
Government argued IoA only dealt with external sovereignty.
Signs of Peace and Security
Reduction in stone pelting and militancy:
Increased security presence and arrests of militants and OGWs.
Fewer terrorist acts.
Reduction in civilian injuries: Fewer injuries from pellet guns and baton charges.
Improved law and order: Fewer law and order incidents.
Way Forward
10-year strategy for education, employment, and employability.
Zero-terror incident plan by 2026.
Adopt Gandhian path of non-violence and peace.
Comprehensive outreach programme to Kashmiris.
Implement Atal Bihari Vajpayee’s Kashmiriyat, Insaniyat, and Jamhooriyat principles.
3. Vision IAS Current Affairs: National Mission for Clean Ganga
Central Idea: NMCG signs MoCP with MRCTI for River Cleanup
Key Facts and Stats
MoCP signed: October 2023
COP28: Dubai
MRCTI: 124 cities on the Mississippi River
RCA: 110 Indian cities and 1 international city
MoJS: Ministry of Jal Shakti
MoHUA: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
NGRBA: National Ganga River Basin Authority
Namami Gange: Program for cleaning Ganga
Clean Ganga Fund: Founded in 2014
Bhuvan-Ganga App: Web app for pollution monitoring
International Collaboration
MoCP with MRCTI: Knowledge exchange for river management
Indian cities learn from MRCTI
MRCTI learns from Indian experiences
River Cities Alliance (RCA):
Indian and international cities
Networking, capacity building, technical support
Launched in 2021 with 30 cities
Now has 111 members
National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG): Objective: Reduce pollution and rejuvenate Ganga River
Programs
Namami Gange: Flagship program
Clean Ganga Fund: Funding for cleanup
Bhuvan-Ganga App: Public involvement in monitoring
Structure:
National Ganga Council (Prime Minister)
Empowered Task Force (Jal Shakti Minister)
State Ganga Committees
District Ganga Committees
Other Initiatives:
Ganga Action Plan (1985)
National River Conservation Plan
National Water Mission (2010)
Ban on Waste Disposal (2017)
River Cities Alliance (RCA)
Objective: Connect river cities and focus on sustainable river development
Three Themes: Networking, Capacity Building, Technical Support
Members: 110 Indian cities, 1 international city
4. Vision IAS Current Affairs: Merit Over Reservation in Appointments of Law Officers
Central Idea: Madras HC rules merit over reservation for law officers.
Key Facts and Stats
Reservation in Public Employment: DoPT requires reservation for appointments exceeding 45 days.
Indra Sawhney case (1992): SC exempted law officers from reservation.
2022 SC ruling: State governments require measurable data for SC/ST promotion reservation.
Article 16(4): Reservation for SC/ST in government services.
Article 16(4B): Carry forward unfilled reserved vacancies.
Article 335: Efficiency of administration must be maintained.
Madras HC Verdict
Merit over Reservation: Government must choose the most competent lawyers.
No Vertical/Horizontal Reservation: Law officers not covered by reservation policy.
Advocate-Client Relationship: Uberrima Fides (utmost good faith) applies.
Law Officer vs. Employee: Law officers are not government employees.
Inclusive Selection Process: Invitation for applications should be open to all.
Reservation in Public Employment
DoPT Office Memorandum (2021): Reservation for appointments exceeding 45 days.
Indra Sawhney case (1992): Law officers exempt from reservation.
2022 SC ruling: Measurable data required for SC/ST promotion reservation.
Constitutional Provisions
Article 15(4) & 16(4): Reservation for SC/ST in government services.
Article 16(4B): Carry forward unfilled reserved vacancies.
Article 335: Efficiency of administration must be maintained.
Additional Notes:
Advocate General: Highest legal officer of a state.
Advocate General qualifications: Must be qualified to be a High Court Judge.
Advocate General powers: Represents state in any court within the state.
Advocate General limitations: No voting rights in state legislature.
Further Expansion:
This mind map can be further expanded upon with more details and visuals as needed.
Additional branches could be added for specific aspects of the judgment or reservation policies.
References and citations could be included for further research.
5. Vision IAS Current Affairs: Mummified Baboons
Central Idea: Mummified baboons reveal ancient trade route and lost city.
Key Facts and Stats:
Origin: Adulis, ancient city in Eritrea
Species: Papio anubis (Anubis baboon) & Papio hamadryas (Hamadryas baboon)
Distribution:
P. anubis: Central sub-Saharan Africa
P. hamadryas: Southern Red Sea region, Ethiopia, Somalia, Eritrea
IUCN Red List: Lower Risk, Least Concern
6. Vision IAS Current Affairs: Project ARTHA Ganga
Central Idea: Sustainable economic model for the Namami Ganga program
Key Facts and Stats:
Launched in 2014
Added as a vertical to Namami Ganga
6 pillars of Arth Ganga
Aims to strengthen river-people connection through economic development
Six Pillars of Arth Ganga
Natural Farming: Promote organic farming on 5 km land on both sides of the river
Treated Water and Sludge: Reuse treated water and sludge from Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs)
Livelihood Opportunities: Improve livelihood opportunities, especially for women
Tourism and Cultural Heritage: Promote tourism and preserve cultural heritage along the river
People’s Participation: Encourage public participation in river conservation and development
Empowering Local Administration: Enhance the capacity of local administration for water governance
Relationship with Namami Ganga: Added as a vertical to the Namami Ganga program
Complements the existing 4 verticals:
Nirmal Ganga (Clean Ganga)
Aviral Ganga (Uninterrupted Flow)
Jan Ganga (Public Participation)
Gyan Ganga (Knowledge Sharing)
Expected Outcomes:
Improved economic conditions for people living near the river
Reduced pollution and improved water quality
Increased environmental awareness and participation
Enhanced cultural heritage preservation
Sustainable development model for river rejuvenation
Additional Notes:
Arth Ganga focuses on creating a win-win situation for both the environment and the local population.
The project relies heavily on public participation and capacity building to achieve its goals.
Arth Ganga is a long-term initiative with the potential to transform the lives of millions of people living along the Ganga River.
For Further Exploration refer:
Official website of the Namami Ganga program
Reports and documents related to Arth Ganga
Research papers on river rejuvenation and economic development
Case studies of successful projects similar to Arth Ganga
What are the objectives of Project ARTHA Ganga?
Promote sustainable economic development along the Ganga River
Improve livelihoods of people living near the river
Strengthen the connection between people and the river
Foster environmental sustainability


